WHAT IS AN APOSTILLE CERTIFICATE?
An Apostille is a certification provided under The Hague Convention of 1961 for authenticating documents for use in foreign countries.
Its only function is to certify the authenticity of the signature of a document.
WHEN CAN THE HAGUE APOSTILLE BE USED?
An apostille may be used only between states which are members of the Multilateral Hague Convention.
The list of states participating in this convention can be found at the bottom of this blog.
A Hague Apostille in needed when:
- The country where the document was issued is party to the Apostille Convention;
- The country in which the document is to be used is party to the Apostille Convention;
- The law of the country where the document was issued considers it to be a public document;
- The country in which the document is to be used requires an Apostille in order to recognition it as a foreign public
NOTE: An Apostille may never be used for the recognition of a document in the country where that document was issued.
An Apostille is only for the use of public documents abroad.
WHAT DOES THE APOSTILLE CERTIFICATE LOOK LIKE?
An apostille is placed directly on the document to be authenticated in the form of a 9×9 centimetre stamp and must always be titled “Apostille” (Hague Convention of 1961).
Generally, the authorities in the designated country will require a translation of the original. In this case, the translation must be certified instead of the original document. Depending on the type of document, you may need a translation from a sworn translator.
This is an example picture of an Apostille:
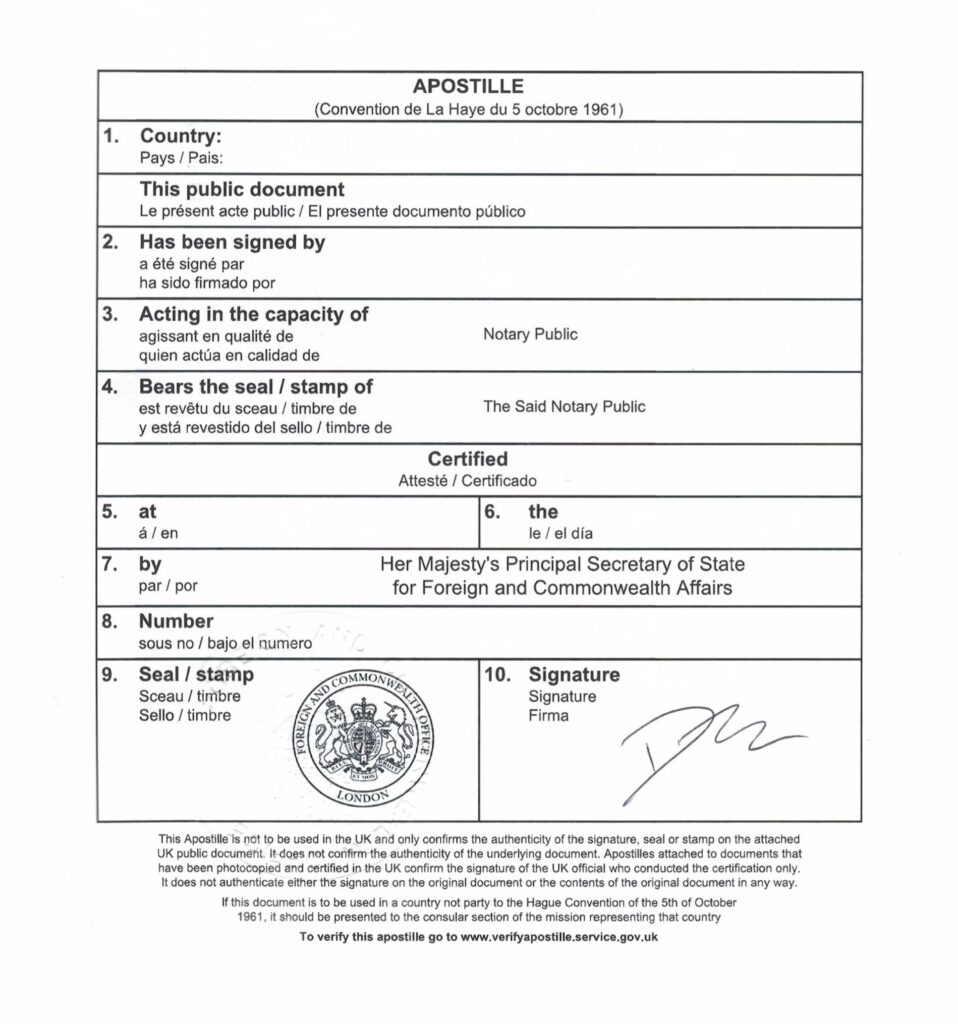
WHICH INFORMATION DOES THE APOSTILLE NEED?
As a legal document, an Apostille Certificate must follow a prescribed format with the following information:
1. Country of issue
2. Who has signed the document
3. The capacity in which the person signed the document
4. Details of any seal on the document
5. Place of issue
6. Date of issue
7. Issuing authority
8. Apostille Certificate number
9. Stamp of issuing authority
10. Signature of representative of issuing authority
WHERE CAN I APPLY FOR AN APOSTILLE?
The application for an apostille must be made by the holder of the document in the document’s country of issue. Each member state of The Hague Convention determines which authorities are responsible for issuing the apostille.
The fees for issuing the apostille also depend on the respective country.
HAGUE APOSTILLE COUNTRY LIST
These are the countries who have signed The Hague Convention:
| A Albania Andorra Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan | L Latvia Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg |
| B Bahamas Bahrain Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burundi | M Macao (China) Macedonia (FYR of) Malawi Malta Marshall Islands Mauritius Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco |
| C Cape Verde Canada Chile China (Hong Kong) China (Macao) Colombia Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic | N Namibia Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niue Norway |
| D Denmark Dominica Dominican Republic | O Oman |
| E Ecuador El Salvador Estonia | P Panama Paraguay Peru The Philippines Poland Portugal |
| F Fiji Finland France | R Republic of Moldova Romania Russian Federation |
| G Georgia Germany Greece Grenada Guatemala | S Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Serbia Seychelles Slovakia Slovenia South Africa Spain Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland |
| H Honduras Hong Kong Hungary | T Tajikistan The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey |
| I Iceland India Ireland Israel Italy | U Ukraine United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK) Uruguay United States of America (USA) Uzbekistan |
| J Japan | V Vanuatu Venezuela |
| K Kazakhstan Korea Kosovo Republic of Kyrgyzstan |


